Function is a database object in SQL Server. Basically, it is a set of SQL statements that accept only input parameters, perform actions and return the result. Function can return an only single value or a table. We can’t use a function to Insert, Update, Delete records in the database table(s).
Types of Function
System Defined Function
These functions are defined by SQL Server for a different purpose. We have two types of system defined function in SQL Server
Scalar Function
Scalar functions operate on a single value and return a single value. Below is the list of some useful SQL Server Scalar functions.
System Scalar FunctionScalar FunctionDescriptionabs(-10.67)This returns an absolute number of the given number means 10.67.rand(10)This will generate a random number of 10 characters.round(17.56719,3)This will round off the given number to 3 places of decimal means 17.567upper('dotnet')This will returns the upper case of given string means 'DOTNET'lower('DOTNET')This will returns the lower case of given string means 'dotnet'ltrim(' dotnet')This will remove the spaces from the left-hand side of 'dotnet' string.convert(int, 15.56)This will convert the given float value to integer means 15.Aggregate Function
Aggregate functions operate on a collection of values and return a single value. Below is the list of some useful SQL Server Aggregate functions.
System Aggregate FunctionAggregate FunctionDescriptionmax()This returns maximum value from a collection of values.min()This returns the minimum value from a collection of values.avg()This returns an average of all values in a collection.count()This returns no of counts from a collection of values.
User Defined Function
These functions are created by the user in the system database or in a user-defined database. We three types of user-defined functions.
Scalar Function
The user-defined scalar function also returns a single value as a result of actions performed by the function. We return any datatype value from a function.
--Create a tableCREATE TABLE Employee(EmpID int PRIMARY KEY,FirstName varchar(50) NULL,LastName varchar(50) NULL,Address varchar(100) NULL,Salary int NULL, ) --Insert DataInsert into Employee(EmpID,FirstName,LastName,Salary,Address) Values(1,'Mohan','Chauahn',22000,'Delhi');Insert into Employee(EmpID,FirstName,LastName,Salary,Address) Values(2,'Asif','Khan',15000,'Delhi');Insert into Employee(EmpID,FirstName,LastName,Salary,Address) Values(4,'Deepak','Kumar',19000,'Noida');Insert into Employee(EmpID,FirstName,LastName,Salary,Address) Values(3,'Bhuvnesh','Shakya',19000,'Noida'); --See created tableSelect * from Employee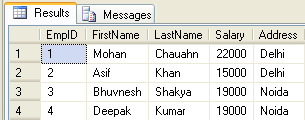 --Create function to get emp full nameCreate function fnGetEmpFullName (@LastName varchar(50)@FirstName varchar(50), ) returns varchar(101) AsendBegin return (Select @FirstName + ' '+ @LastName);
--Create function to get emp full nameCreate function fnGetEmpFullName (@LastName varchar(50)@FirstName varchar(50), ) returns varchar(101) AsendBegin return (Select @FirstName + ' '+ @LastName); --Calling the above created functionSelect dbo.fnGetEmpFullName(FirstName,LastName) as Name, Salary from Employee
--Calling the above created functionSelect dbo.fnGetEmpFullName(FirstName,LastName) as Name, Salary from Employee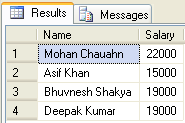
Inline Table-Valued Function
The user-defined inline table-valued function returns a table variable as a result of actions performed by the function. The value of the table variable should be derived from a single SELECT statement.
--Create function to get employeesCreate function fnGetEmployee()return (Select * from Employee)returns TableAs --Now call the above created functionSelect * from fnGetEmployee()
--Now call the above created functionSelect * from fnGetEmployee()
Multi-Statement Table-Valued Function
A user-defined multi-statement table-valued function returns a table variable as a result of actions performed by the function. In this, a table variable must be explicitly declared and defined whose value can be derived from multiple SQL statements.--Create function for EmpID,FirstName and Salary of EmployeeCreate function fnGetMulEmployee() returns @Emp Table (Insert into @Emp Select e.EmpID,e.FirstName,e.Salary from Employee e;EmpID int, FirstName varchar(50), Salary int ) As beginupdate @Emp set Salary=25000 where EmpID=1;--Now update salary of first employeeend--It will update only in @Emp table not in Original Employee tablereturn --Now call the above created functionSelect * from fnGetMulEmployee()
--Now call the above created functionSelect * from fnGetMulEmployee()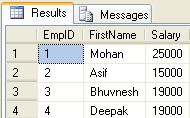 --Now see the original table. This is not affected by above function update commandSelect * from Employee
--Now see the original table. This is not affected by above function update commandSelect * from Employee
Note
Unlike Stored Procedure, Function returns an only single value.
Unlike Stored Procedure, Function accepts only input parameters.
Unlike Stored Procedure, Function is not used to Insert, Update, Delete data in a database table(s).
Like Stored Procedure, Function can be nested up to 32 levels.
User Defined Function can have upto 1023 input parameters while a Stored Procedure can have upto 2100 input parameters.
User Defined Function can't return XML Data Type.
User Defined Function doesn't support Exception handling.
User Defined Function can call only Extended Stored Procedure.
User Defined Function doesn't support set options like set ROWCOUNT etc.

No comments:
Post a Comment
It’s all about friendly conversation here at small review :) I’d love to be hear your thoughts!
Be sure to check back again because I do make every effort to reply to your comments here.