SQL Keys are a single or combination of multiple fields in a table. They allow you to create a relationships between two or more tables and maintain uniqueness in a table.
It is used retrieve data from the table according to the condition and also they are responsible for to keep consistent and valid data in database.
1. Primary Key
A Primary key is a column or a group of columns that uniquely identifies each row in a table. It contain UNIQUE values in column, and does not allows NULL values.
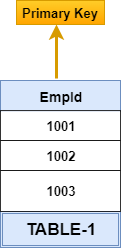
Primary Key
In Table-1, Empid is a Primary Key. In SQL Server, by default primary key creates a clustered index.
Each table can have only one Primary key and multiple Candidate keys
2. Candidate Key
Candidate Key can be defined as a set of one or more columns that can identify a record uniquely in a table and which can be selected as a primary key of the table.
It contains UNIQUE values in column, and does not allows NULL values.

Candidate Keys
In Table-1, Empid, EmpLicence and EmpPassport are candidate keys.
3. Unique KeyUnique key is similar to primary key and does not allow duplicate values in the column.
Comparison with Primary Key
- It allows one null value in the column.
- By default, it creates a non-clustered index on heap tables.
4. Alternate Key
Alternate key can be defined as a key that can be work as a primary key if required but right now it is not Primary key.
Example: In Table-1, Empid is primary key but we can use EmpLicence & EmpPassport as a primary key to get unique record from table, That’s why EmpLicence & EmpPassport are Alternate keys but right now it is not primary keys.
5. Composite/ Compound Key
Composite Key is a combination of more than one columns of a table. It can be a Candidate key and Primary key.
Example: In Table-1, we can combine Empid & EmpLicence columns to fetch the data from table.
6. Super Key
A super key is a group of single or multiple keys which identifies rows in a table.

Super Key
Example: In Table-1, Primary key, Unique key, Alternate key are a subset of Super Keys.
{Empid, Empname}, {Empid, EmpPassport, Empname}, {EmpLicence, Empname}
Any set of column which contains EmpLicence or EmpPassport or Empid is a super key of the table.
7. Foreign Key
Foreign creates a relationship between two or more tables, a primary key of one table is referred as a foreign key in another table.
It can also accept multiple null values and duplicate values.

Foreign Key
Example: In Table 1, Did column(Foreign key) is points to Did column(Primary key) of Table-2.


No comments:
Post a Comment
It’s all about friendly conversation here at small review :) I’d love to be hear your thoughts!
Be sure to check back again because I do make every effort to reply to your comments here.