A key is a single or combination of multiple fields in a table. It is used to fetch or retrieve records/data-rows from data table according to the condition/requirement. Keys are also used to create a relationship among different database tables or views.
Types of SQL Keys
We have following types of keys in SQL which are used to fetch records from tables and to make relationship among tables or views.
Super Key
Super key is a set of one or more than one keys that can be used to identify a record uniquely in a table. Example: Primary key, Unique key, Alternate key are a subset of Super Keys.
Candidate Key
A Candidate Key is a set of one or more fields/columns that can identify a record uniquely in a table. There can be multiple Candidate Keys in one table. Each Candidate Key can work as Primary Key.
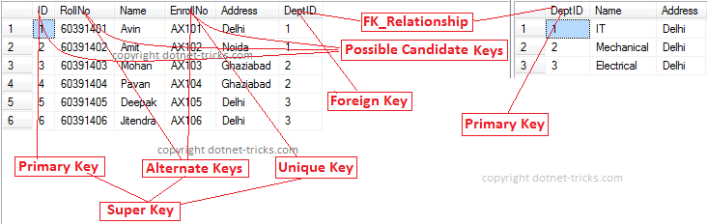
Example: In the below diagram ID, RollNo and EnrollNo are Candidate Keys since all these three fields can be work as Primary Key.
Primary Key
Primary key is a set of one or more fields/columns of a table that uniquely identify a record in a database table. It can not accept null, duplicate values. Only one Candidate Key can be Primary Key.
Alternate key
An Alternate key is a key that can be work as a primary key. Basically, it is a candidate key that currently is not a primary key.
Example: In the below diagram RollNo and EnrollNo become Alternate Keys when we define ID as Primary Key.
Composite/Compound Key
Composite Key is a combination of more than one fields/columns of a table. It can be a Candidate key, Primary key.
Unique Key
A unique key is a set of one or more fields/columns of a table that uniquely identify a record in a database table. It is like Primary key but it can accept only one null value and it can not have duplicate values. For more help refer to the article Difference between primary key and unique key.
Foreign Key
Foreign Key is a field in a database table that is Primary key in another table. It can accept multiple null, duplicate values. For more help refer to the article Difference between primary key and foreign key.
Example: We can have a DeptID column in the Employee table which is pointing to a DeptID column in a department table where it a primary key.
Defining Keys in SQL Server
--Department Table CREATE TABLE Department ( DeptID int PRIMARY KEY, --primary key Name varchar (50) NOT NULL, Address varchar (200) NOT NULL ) --Student Table CREATE TABLE Student ( ID int PRIMARY KEY, --primary key RollNo varchar(10) NOT NULL, Name varchar(50) NOT NULL, EnrollNo varchar(50) UNIQUE, --unique key Address varchar(200) NOT NULL, DeptID int FOREIGN KEY REFERENCES Department(DeptID) --foreign key )
Important Note
Practically in the database, we have only three types of keys Primary Key, Unique Key and Foreign Key. Other types of keys are only concepts of RDBMS which you should know.

No comments:
Post a Comment
It’s all about friendly conversation here at small review :) I’d love to be hear your thoughts!
Be sure to check back again because I do make every effort to reply to your comments here.